Contractors across the professional trade industries have likely heard of VRF systems on the job, but might be wondering what exactly VRF is and how it works. Even though it has been widely used in other countries for over 30 years, VRF, which stands for variable refrigerant flow, has only been available in the United States since the early 2000s. VRF is known for its superior energy efficiency and ability to offer a quick return on investment in many applications. Whether you’re an HVAC contractor, a builder or a mechanical contractor, leveraging VRF technology will allow you to deliver a state-of-the-art HVAC solution for your customers. Learn what VRF is, how it works, and read common VRF myths and facts to see how you and your customers can benefit from VRF on your next project.
VRF explained
Complexity is the name of the game when describing the technical nature of how variable refrigerant flow technology works. The simplest explanation of VRF is to describe it as a large-scale ductless HVAC system that can perform at a high capacity. The specific design of a VRF system varies based on application. In general, VRF technology provides the ability for multiple indoor units or zones to operate on the same system. VRF systems can either be a heat pump system or a heat recovery system, which provides simultaneous heating and cooling.
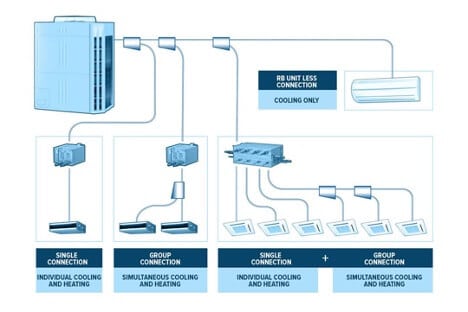
Because of their versatility, VRF products can be customized to meet the specific demands of virtually any project.
VRF HVAC technology myths & facts
- Fact: VRF systems provide simultaneous heating and cooling.
A VRF HVAC system can heat and cool different zones or rooms within a building at the same time. If the appropriate VRF system is selected, building occupants have the ability to customize the temperature settings to their personal preferences. - Myth: VRF can only be used in commercial applications.
VRF equipment can be used in conjunction with a wide range of heating and cooling products. This means that a VRF system can be scaled to meet the climate control needs of a small single-family residence all the way to a commercial high-rise building. - Fact: VRF systems run at a very low volume.
Unlike some older HVAC technologies, VRF systems are extremely quiet. Installing a VRF system has the added benefit of reducing ambient noise both inside and outside of a building. - Myth: VRF HVAC units are bulky.
VRF equipment is sleek and compact compared to other HVAC equipment. This makes VRF an excellent solution for installing HVAC equipment in areas with limited space, such as when renovating historical buildings. - Fact: VRF systems are easy to install.
Because VRF equipment weighs much less than ducted equipment, installing a VRF system is easier and requires less physical effort than a traditional HVAC system.
Pro tip: VRF installation should only be performed by professionals who are factory trained and certified based on the type of VRF system being implemented.


